Your doctor may prescribe it along with a special diet if your blood cholesterol level is high enough to put you in danger of heart disease, and you have been unable to lower your cholesterol by diet alone.
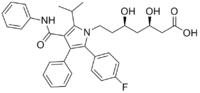
[R-(R*, R*)]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta, delta-dihydroxy-5- (1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4- [(phenylamino)carbonyl]-1H- pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid
The drug works by helping to clear harmful low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol out of the blood and by limiting the body's ability to form new LDL cholesterol.
Lipitor ® should be taken once a day, with or without food. You can take it in the
morning or the evening, but
should hold to the same time each day. The drug generally begins working within 2 weeks.
Take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the one you missed and go back to your regular schedule. Never take 2 doses at the same time.
Side effects cannot be anticipated. If any develop or change in intensity, inform your
doctor as soon as possible. Only your doctor can determine if it is safe for you to
continue taking Lipitor ® . The side effects of Lipitor ® -if any develop-are usually mild.
Side effects may include:Abdominal pain, allergic reaction, back pain, changes in
eyesight, cold, constipation, diarrhea, dry eyes, dry skin, flu symptoms, gas, hair loss,
headache, heartburn, indigestion, inflammation of sinus and nasal passages, itching, joint
pain, leg cramps, muscle aching or weakness, purple or red spots on the skin, rash, sore
throat, urinary problems, vomiting.
Never take Lipitor ® during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. You should also avoid Lipitor ® if you have liver disease, or if the drug gives you an allergic reaction.
The usual starting dose is 10 milligrams once a day, with or without food. The doctor will check your cholesterol levels every 2 to 4 weeks and adjust the dose accordingly. The maximum recommended daily dose is 80 milligrams.
There is a slight chance of liver damage from Lipitor ® , so your doctor may order a blood
test to check your liver function before you start taking the drug, again 6 weeks and 12
weeks after you begin therapy or your dosage is increased, and every 6 months thereafter.
If the tests reveal a problem, you may have to stop using the drug.
Drugs like Lipitor ® have occasionally been known to damage muscle tissue, so be sure to
tell your doctor immediately if you notice any unexplained muscle tenderness, weakness, or
pain, especially if you also have a fever or feel sick. Your doctor may want to do a blood
test to check for signs of muscle damage.
Common adverse drug reactions (≥1% of patients) associated with atorvastatin therapy include: myalgia, mild transient gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, constipation, passing gas), elevated hepatic transaminase concentrations, headache, insomnia, joint pain, and/or dizziness.
Myopathy and rhabdomyolysis occur in <0.1% of patients. Risk is increased in patients with renal impairment, serious concurrent illness; and/or concomitant use of drugs which inhibit CYP3A4.
![]()