- The treatment of androgenic alopecia
and hairloss
-
-
The best in the world at the best
price!
-
Recent research indicates that the DHT that harms hair
follicles comes from the the skin's sebocytes and sweat glands (sebaceous glands).
(Chen et al 1996) 5 alpha-Reductase, the enzyme system that converts
testosterone into DHT occurs into two enzyme forms. Type 1 represents the 'cutaneous
type'; it is located primarily in the skin's sebocytes but also in epidermal and
follicular keratinocytes, dermal papilla cells and sweat glands as well as in
fibroblasts. Type 2 is located mainly in the seminal vesicles, prostate and in
the inner root sheath of the hair follicle.
- f.
- Inhibiting the union of the DHT with
the citosilic receptors of the follicles. The receptor is a protein that
bind the DHT. Some studies affirm that this receptor is present under
form of tetramero and monomero. The tetramero is inactive, while the
monomero is being active.There is a enzymatic chain that converts the
tetramero in monomero. Bald people have more monomero receptors for
the DHT. A solution for this is the
spironolactone
or Revivogen.
- Using the so-called "growth stimulator" as the
minoxidil,
NANO,
SOD, tripeptide
copper-complex, contained for example in
Revivogen,
Remox,
Corvinex,
Promox, Proxiphen, Proxiphen-N,
Folligen,
Tricomin,
Keracyte-b, etc. it increase
the internal levels of
nitroxides.
- Interfering with the local autoimmune reaction, for
example acting against the free superoxide radical, product in abundance
during an autoimmune attack, with scavenger SOD, using for example Proxiphen,
Proxiphen-N, Folligen, Tricomin, etc.
Please, read also
Top 5
hairloss treatments.
With the therapy, sometimes, it is possible to assist to
the inversion of the follicle miniaturization, then the progressive enlargement
and the formation of hair bigger, more pigmented, up to hair type
terminal.
It is important that therapy is mixed, striking the
problem from the varied anglings, in particular way if baldness is advanced.
Estrogens, the feminizing hormones, can inhibit or
counteract the follicle-shrinking effect of the androgens. Women have more
estrogens circulating in their blood than men. Women having a genetic
predisposition for pattern hair loss are protected from losing their hair
because of the high level of estrogens in their blood. When these women reach
menopause however, their estrogens level may decrease and the protective effect
may be overridden by the DHT message. Then hair can begin to thin rapidly. Some
women are genetically pre-disposed to have pattern hair loss.
This type of hair loss or Androgenetic Alopecia or pattern
baldness affects over 70% of men but also 15% of women. Women usually do not
develop bald spots, but rather have overall thinning hair. Over 50% of the hair
can be lost before the results are readily apparent.
Estrogens help to restore the emotional and physical
condition of the patient to the pre-menopause states. It may also slow or stop
hair loss triggered by menopause. Hormone replacement therapy has been a
controversial treatment for menopause but newer methods are finding reductions
in the risk of some cancers and in the risk of heart diseases.
The best known DHT (dihydrotestosterone) blocker is
Propecia®,
a drug from Merck, but Merck does not recommend Propecia for women: a one year
study of hair growth in 136 post-menopausal women found no significant effect of
Propecia on hair growth.
Whether thinning, receding, or completely gone, hair loss is often tied into
heredity and various environmental factors. For some people, it starts later in
life. For others, hair loss may begin to occur during early adulthood.
- What Causes Hair Loss?
- The normal hair growth cycle is 2 to 6 years long. About 90 percent of the
hair in the scalp is in a "growing" phase and 10 percent is in a "resting" phase.
Some hair is lost every day as part of this growing and resting cycle.
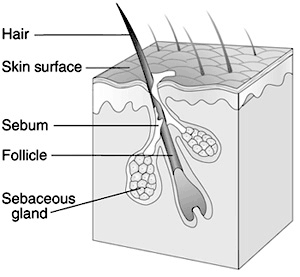
- Excessive hair loss is often caused by the male hormone testosterone which
interacts in the scalp with the enzyme 5-alpha reductase to form the
aging-bio-marker DHT, or Dihydrotestosterone. This transformed hormone signals
the hair follicles in the scalp (by a mechanism that is not yet understood) to
begin a process called follicular miniaturization. This course of hair thinness
and loss sometimes begins as early as puberty, and about a quarter of men begin
to show symptoms by age 30, while two-thirds of men over 60 are either bald or
show a balding pattern. This form of "Pattern Baldness" is a primary cause of
baldness, although exposure to environmental factors and UV light can also contribute significantly to hair loss.
- Solar radiation and associated Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the skin of
the scalp activate a breakdown in the number of cells that produce hair, as well
as the destruction of elastin and other Matrix Proteins surrounding and
supporting the hair follicles. As these destructive elements impact the cells in
the scalp, they trigger the initial effects of balding. The hair follicles
become smaller. Hair loses its color, and the hair shafts become thin, fragile
and begin to resemble peach fuzz. That’s why it is important to maintain the
health and vitality of your scalp and hair – it’s much easier to keep the hair
you have than it is to regrow the hair you’ve lost. Keracyte-b provides
nutrients to your scalp that help maintain follicle health, including
Recombinant Human Tropoelastin, or Elastatropin., to replenish the essential
elastin in your scalp that supports, maintains and connects it’s network of hair
follicles and healthy head of hair.
The Hair Life Cycle
Hair follicles repeatedly go through stages in a cycle of growth and
resting. It is the disruption of this cycle that results in excessive hair
loss, or alopecia. The specialized cells in the follicle that become the
hair shaft itself can be depleted during the resting or Latent phase in the
hair cycle, resulting in less and less active follicles (and hair) over time.
-

- ANAGEN.
- The hair growing stage is called Anagen.
-
- The bottom of the hair follicle
(the bulb) is attached to the dermis and its blood supply through the dermal
papilla.
-
- The precursor cells, called keratinocytes, and assocated
melanocytes multiply at the bottom of the bulb.
-
- The growing keratinocytes
become part of the hair shaft. The upward pressure of the multiplying
keratinocytes pushes the shaft up out of the follicle, where is appears as a
hair.
-
- Hair grows outward from the bulb at about 1 cm per month. The Anagen
phase lasts 3 years on average but can vary from a few months to as much as
ten years.
-
- The length of time the hair follicle remains in Anagen, and keeps
growing, depends on the signals it receives from the surrounding scalp and
its blood supply.
-
- The cells that make up the hair follicle also communicate
via the fibers in the Extracellular Matrix that provides the structure of
the skin in the scalp.
-
- The hair follicle then enters the next phase of the
cycle.
-
-
-
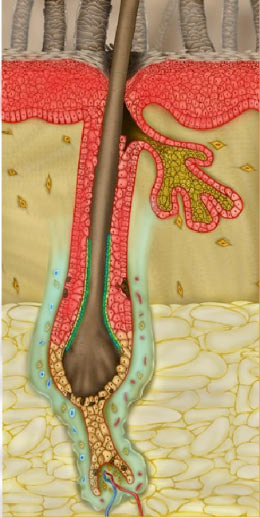 CATAGEN.
CATAGEN.
- When matrix cells in the hair follicle exhaust their
proliferative capacity or chemical signals are received from the skin or
blood, hair growth stops.
-
- The hair follicle begins to die and enters the
CATAGEN phase.
-
- This process of programmed cell death or apoptosis,
results in the lower two-thirds of the hair follicle degenerating.
-
- The cells remaining form a pocket surrounding the old
hair.
-
- This process occurs in a matter of a few weeks.
-
- The “bulb” of the hair follicle is drawn toward the
skin surface via fibers in the Extracellular matrix, and essentially
separates from the dermal papilla.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
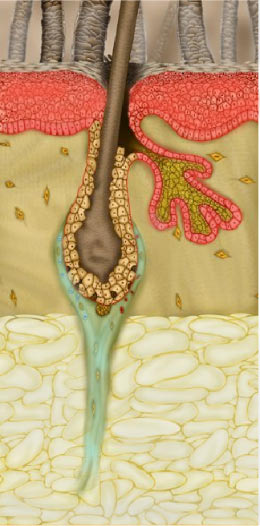 TELOGEN.
TELOGEN.
- In the Telogen phase, the remains of the hair bulb
are inactive and the attached hair easily falls out.
-
- The telogen phase can last for 2 to 3 months.
-
- In the meantime, the dermal papilla remains attached
to the remains of the bulb through the interconnecting network of the
Extracellular Matrix.
-
- The fibers in this matrix maintain both a structural
linkage and a chemical communication between the two components of the
hair follicle.
-
-
 LATE
TELOGEN.
LATE
TELOGEN.
- In the final phase of Telogen, lasting a few weeks, a
chemical signal causes the “bulge” and dermal papilla to re-assemble
within the scalp Matrix and form a new hair follicle around the empty
follicle.
-
- Stem cells within their reservoir in the bulge begin
to form new keratinocytes and the cycle starts over with a new Anagen
phase.
-
- It is during the “re-awakening” process that stem
cells can die and the hair follicles lose the capacity to form a new
hair shaft.
-
- Preventing the loss of keratinocyte stem cells is
extremely important to altering the course of hair loss and baldness.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hair transplants and other surgical procedures to
treat balding are performed by a physician in a surgical environment.
Hair transplants remove growing hair from one part of the head and
transfer it to another area that has less hair cover. This is a somewhat
painful and fairly expensive procedure, but has the advantage that it is
usually permanent. Hair weaves, hair pieces, articifical har replacement
or changes of hair style may disguise hair loss. These are the least
expensive and safest approach to hair loss. These approiaches are also
temporary and can look somewhat artificial. Hair pieces and other
appliances are also inconvenient and occasionally embarrassing to use.
Association of
androgenetic alopecia and hypertension.

 CATAGEN.
CATAGEN.
 TELOGEN.
TELOGEN.
 LATE
TELOGEN.
LATE
TELOGEN. 

